By: Dr. Robert G. Cooper
Too many initiatives within the growth pipeline is a standard however severe criticism in new-product growth departments. Pipeline gridlock results in under-resourced growth initiatives, which find yourself taking too lengthy to get to market, after which typically under-perform. Options are supplied—Gates with Tooth, Pink Flags, and the Productiveness Index—to attain a extra balanced growth pipeline with fewer initiatives however higher initiatives.
Too Many Tasks within the Pipeline
Portfolio administration is about translating your corporation’s innovation technique into funding selections on particular new-product initiatives. Since its popularization within the mid-Nineties, new-product portfolio administration has confronted various challenges, as business struggled to get it proper. Essentially the most continuously cited problem is pipeline gridlock—that’s, just too many growth initiatives within the pipeline for the obtainable assets.1,2,3,4 Portfolio managers are “usually involved and overwhelmed with points just like the prioritization of initiatives and the continual distribution of personnel from the totally different initiatives to beat the pressing crises.”5 The result’s that folks assets are unfold too thinly throughout too many initiatives, so that each undertaking, even the essential ones, are under-resourced.6 The shortage of wanted assets is likely one of the basic the explanation why initiatives take so lengthy to get to market, and can also be blamed for shortcuts taken to save lots of effort and time, that later come again to hang-out the undertaking workforce.7
The Function of New-Product Portfolio Administration
The accepted definition in prior analysis states that “new-product portfolio administration is a dynamic resolution course of, whereby a enterprise’s listing of lively new-product (R&D) initiatives is consistently up to date and revised. On this course of, new initiatives are evaluated, chosen, and prioritized; current initiatives could also be accelerated, killed or deprioritized; and assets are allotted and reallocated to the lively initiatives.”8,9 The PDMA Handbook definition is far the identical.10
A Failure to Kill Dangerous Tasks
One of many causes for too many growth initiatives is the failure to kill unhealthy initiatives in a well timed style. Tasks typically look good at their starting, and thus many are initially accepted.11 Over time and as soon as into growth or past and as new data turns into obtainable, a few of these “accepted initiatives” lose their luster. By now, nevertheless, the undertaking has momentum: They get “a lifetime of their very own” and proceed although growth regardless, the results of firm politics; govt stress; sunk value reasoning; monetary causes (it’s within the finances!); emotion and enthusiasm by the undertaking workforce or administration; or just the shortage of a kill mechanism within the course of.12 Thus, stopping such initiatives midway via growth or past is like making an attempt to halt an specific practice at full pace.
Fewer Tasks, Higher Tasks!
To maximise R&D productiveness, the reply is to focus your assets: Undertake fewer initiatives however higher initiatives, useful resource them correctly, and get them achieved proficiently and in a well timed style. (Right here “productiveness” is “output for a given enter,” for instance “profitability per R&D {dollars} spent”). An admirable objective, however robust to attain. Three confirmed options that assist eradicate weaker initiatives and yield focus embrace:
- Actual time monitoring and monitoring of initiatives – to identify initiatives in bother and to take the wanted motion early. Typically the choice can be Kill, and to re-allocate the assets to increased worth, extra meritorious initiatives, the online consequence being a extra productive portfolio. However what metrics ought to one use to trace these initiatives?
- Harder gates – designed to weed out the weaker, decrease worth initiatives earlier than spending extra money on them within the subsequent stage. However how does one operationalize “gates with tooth?”
- Common portfolio critiques, with a rigorous rating and prioritization of initiatives based mostly on worth. The result’s a shorter listing of higher initiatives and a extra productive portfolio. However how does one power rank a set of assorted initiatives in opposition to one another?
Let’s see how every answer works in apply.
Monitoring Tasks in Actual Time
One answer is to watch new-product initiatives on an on-going foundation and to kill the unhealthy initiatives in actual time.13 This is likely one of the keys to avoiding overloading the event pipeline. However what metrics does one use to watch initiatives over time? Too many companies gauge the continued advantage of a undertaking on the idea of conventional undertaking administration metrics: assembly milestones (on schedule) and staying inside finances. The acquainted visitors mild utilized in undertaking administration—pink, yellow and inexperienced lights to sign behind or on schedule—is an instance. If the undertaking is “on schedule and on finances,” then all is okay and the default resolution is “proceed.”
Merely staying on schedule and inside finances is a poor cause to proceed spending on the undertaking, nevertheless: A undertaking could also be on schedule and inside finances, however as a result of the enterprise case has modified might have turn into a unhealthy funding and ought to be killed. Slightly, the necessity right here is to find out and monitor the financial well being or worth of the undertaking because it strikes ahead.
Monitor the Productiveness Index
The Productiveness Index (PI) is a helpful metric to gauge the financial well being of a undertaking in a dynamic, actual time approach. The PI is just the worth of the undertaking divided by the constraining useful resource, normally person-days or {dollars}. It gauges what worth is added for each extra unit of scarce useful resource—person-days or {dollars}—that’s spent on the undertaking. In impact, the PI gauges the “bang for buck:”

In apply, one merely takes the estimated NPV from the undertaking’s Enterprise Case, up to date because the undertaking strikes ahead, and divides by the person-days or {dollars} that have to be spent as a way to full the undertaking. Notice that sunk prices aren’t related to the dedication of the PI, solely the “go ahead” prices and person-days are counted.
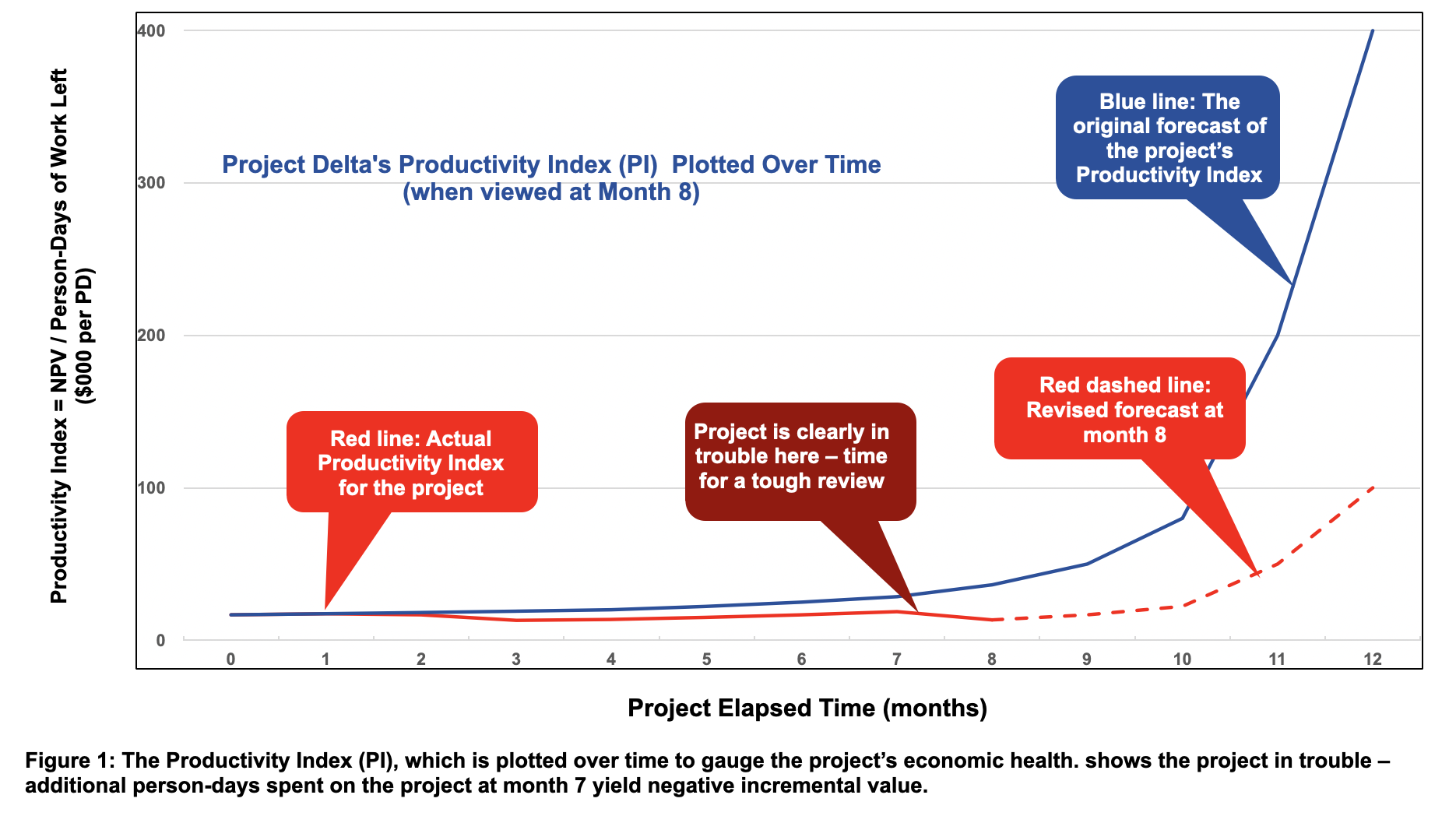
Instance: Mission Delta is tracked over time for its one-year growth, utilizing its Productiveness Index (PI) proven in pink in Determine 1. The PI begins out at $16.7K per per-day on the level of undertaking approval (at month zero), and ideally ought to observe the blue line, steadily upwards (the blue line is the unique forecast). Notice that as one approaches the top of the event (month 12), there stay fewer and fewer particular person days of labor stay to be achieved, so the blue line forecast begins to rise shortly because the PI’s denominator approaches zero.
Round month 7, nevertheless, Mission Delta will get into bother: The Enterprise Case is revised downwards attributable to less-than-enthusiastic buyer suggestions on early prototypes, and likewise the variety of days to finish the undertaking will increase as a result of some duties are taking longer than forecasted. So, round month 7, the pink line in Determine 1 begins to dip—the extra particular person days spent yield damaging incremental worth—and thus indicators that it’s time for a tricky rethink of this undertaking. The revised PI forecast for the remainder of the undertaking (the pink dashed line) can also be disappointing. A direct Go/Kill gate assembly is scheduled.
Use Pink Flags to Spot Tasks in Hassle
Monitoring the undertaking’s financial well being with the PI is a really helpful method to sign a possible kill resolution, however different damaging conditions may also happen. What occurs when a undertaking misses milestones, or its technical feasibility drops inside a stage? Do you wait till the subsequent gate to handle the issue and kill or redirect the undertaking? Positively not! An efficient answer is to make use of a system of pink flags in order that motion will be taken, and there are not any surprises when the undertaking reaches the subsequent gate evaluation. A pink flag right here is very similar to a pink flag at an auto racetrack. When the pink flag is dropped, each driver takes motion: There’s an emergency on the racetrack, and all of the race automobiles should cease.
Pink flags work a lot the identical approach for new-product initiatives.14 At any time when a undertaking will get into bother, the undertaking chief is required to “throw out a pink flag.” The flag is picked up instantly by the PMO Supervisor (Mission Administration Workplace) or Course of Supervisor, who meets with the workforce chief to debate the seriousness of the state of affairs; they alert the gatekeepers (senior administration), and an emergency gate assembly could also be scheduled. The notion right here is to not wait out the state of affairs, however to take instant motion to appropriate the issue or to kill or redirect the undertaking.
A pink flag is triggered by various damaging circumstances, for instance a major lower in anticipated gross sales or profitability, falling delayed, going over finances, hitting technical roadblocks, or having to omit key product options. At any time when any of those pink flag circumstances happen, the undertaking chief throws out a pink flag.
Construct In “Gates with Tooth”
Though your organization may need put in a Stage-Gate system to drive new product initiatives to market, the gates are sometimes both non-existent or lack tooth.15 The explanation: Administration doesn’t know the best way to say “no!” Thus, although gate conferences are held with one of the best of intentions—to supply a vital analysis of the undertaking and make a Go/Kill resolution—the Kill possibility is never exercised. And just like the addictive poker participant who doesn’t know when to fold his hand and stroll away from the desk, there are a lot of good (and never so good) excuses for persevering with to push the undertaking onward. Even worse, in lots of companies we’ve got investigated, there was by no means an intention to kill a undertaking as soon as underway. After the preliminary Go resolution, the gates quantity to little greater than a undertaking evaluation assembly, an replace for administration, or a milestone checkpoint, however not a severe Go/Kill and funding resolution assembly.
Commit the Folks Sources at Gates… Actually!
Gates aren’t merely undertaking critiques nor undertaking milestones. A milestone, because the time period suggests, is a test that the undertaking is on time (and on finances); however it’s not a Go/Kill resolution level. Slightly, that’s the position of a gate: A gate is an funding resolution, a call to commit folks and funds: a agency dedication of assets to a undertaking chief and workforce to execute the subsequent stage of the undertaking.
So make it a rule: If the gate resolution is Go, then the assets have to be dedicated. If the folks assets aren’t obtainable (now or within the instant future), the undertaking can’t be given a Go resolution. A Go resolution with out a useful resource dedication is a “hole Go resolution.” The results of such hole Go selections—Go with out assets dedicated—is that there is no such thing as a restrict to the provision of individuals, and thus too many initiatives get accepted. However by realizing the restrict on complete folks assets obtainable, and intentionally allocating a few of these folks to particular initiatives at every gate assembly, an automated restrict exists to the variety of initiatives that administration can approve.
Monitor the Sources Dedicated
An essential process of the PMO or Course of Supervisor is to maintain monitor of useful resource allocations by undertaking and by particular person. Somebody from the PMO normally attends every gate assembly, typically because the gate facilitator. If assets actually are dedicated on the gate, then they will report these useful resource commitments—folks, person-days and funds. Then it’s a matter of protecting monitor of those numbers. Whereas useful resource administration software program exits, a easy spreadsheet, one web page per 30 days, may also do the job (see Determine 2). Right here, persons are famous throughout the highest of the sheet, and initiatives are down the left facet. The variety of person-days in famous for every row and column, based mostly on the selections made on the gate assembly.
The PMO supervisor can now test to see that people aren’t overloaded, and she will additionally see what number of assets are going to every undertaking (versus what was requested by the undertaking chief on the gate assembly). This data is beneficial when assigning folks to initiatives at gate conferences. For instance, three folks in Determine 2 are closely overloaded—their complete assigned days add to greater than 100% every for the month (famous in pink) and thus these three folks can’t be assigned to any extra initiatives.
As well as, it typically turns into very clear {that a} undertaking is closely under-resourced. For instance, in Determine 2, three new-product initiatives have lower than one FTE (full-time equal folks) every, which seemingly means they’re useful resource poor (famous in orange).
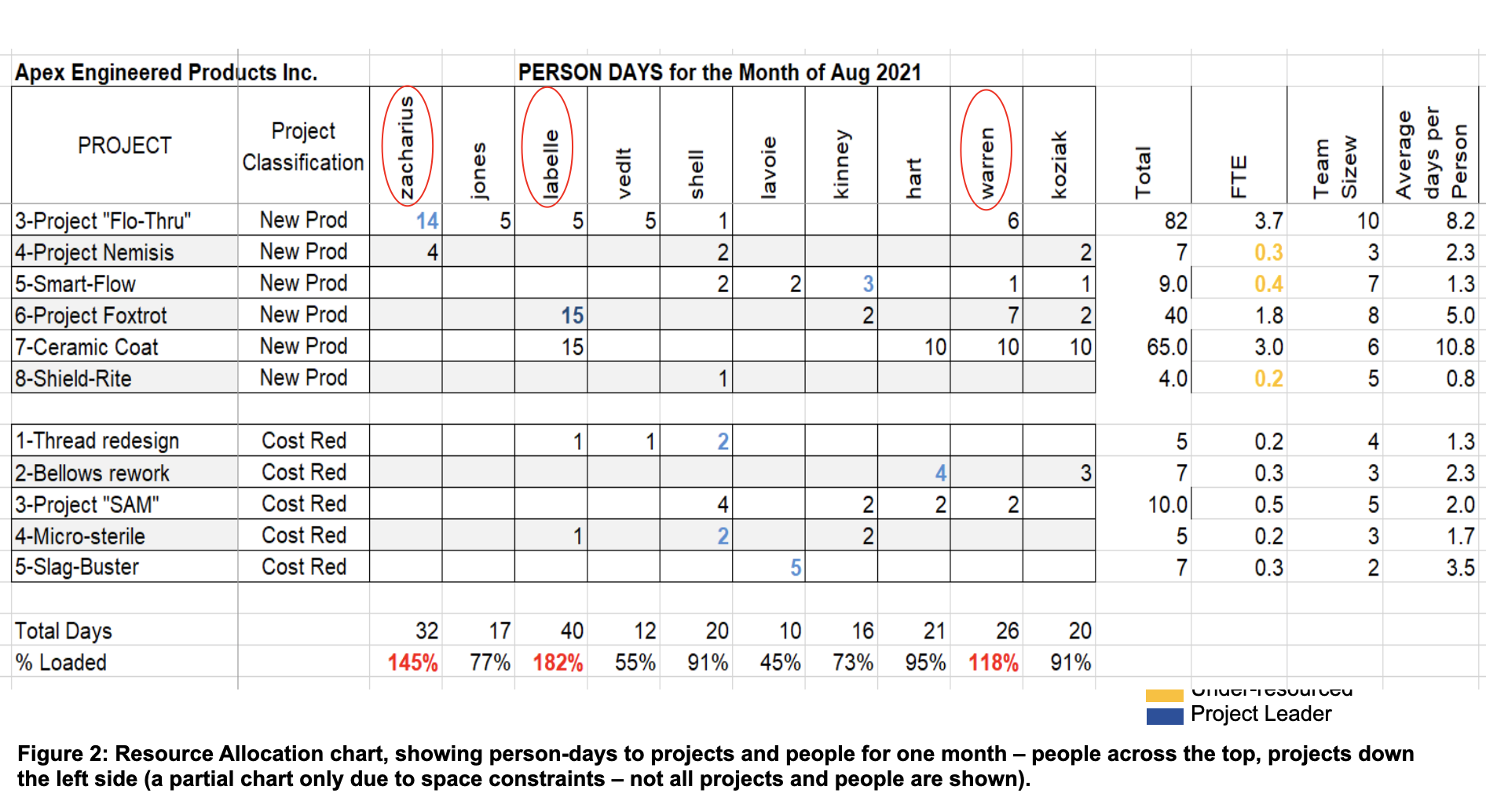
By protecting monitor of individuals and commitments in such a chart, the PMO supervisor is in a a lot better place to advise on task of individuals at gate conferences, and likewise which initiatives might have extra assets at gate and portfolio evaluation conferences. On this Determine 2 instance, the three closely under-resourced new-products had been placed on maintain, and one other low worth undertaking was terminated, slicing the variety of new-product initiatives from 8 all the way down to 4. The freed-up assets had been then re-allocated to higher initiatives, thereby considerably assuaging their useful resource deficiencies.
Apply Seen Go/Kill Standards at Gates
Choices made at gates are fairly often unsuitable. For instance, the PDMA estimates that for each 4 initiatives that enter the heavy-spending Improvement stage, just one turns into a business success (the opposite three both are later cancelled, typically after appreciable assets have been spent, or fail out there).16 This success fee of “one proper resolution out of 4” wants enchancment.
One method to sharpen the gate resolution is the use of seen standards for go. Standards for go aren’t simply “readiness test” inquiries to test that sure deliverables are in place or duties accomplished, however are robust standards that take a look at the attractiveness of the undertaking from an funding perspective.
Monetary Standards: Most companies use NPV or an identical metric to assist make the funding selections on new-product initiatives. The issue with such monetary sure is not the strategy, however the knowledge. Certainly the restricted analysis achieved right here exhibits that when monetary fashions are utilized to new-product initiatives, the outcomes are historically unreliable, particularly pre-development when the important thing funding selections have to be made.17 Thus, monetary fashions are helpful in that they supply a sign of the undertaking’s business prospects, and infrequently reveal how a lot is unknown in regards to the undertaking; but when Go/Kill selections are made based mostly solely on monetary standards, anticipate many unsuitable gate selections!
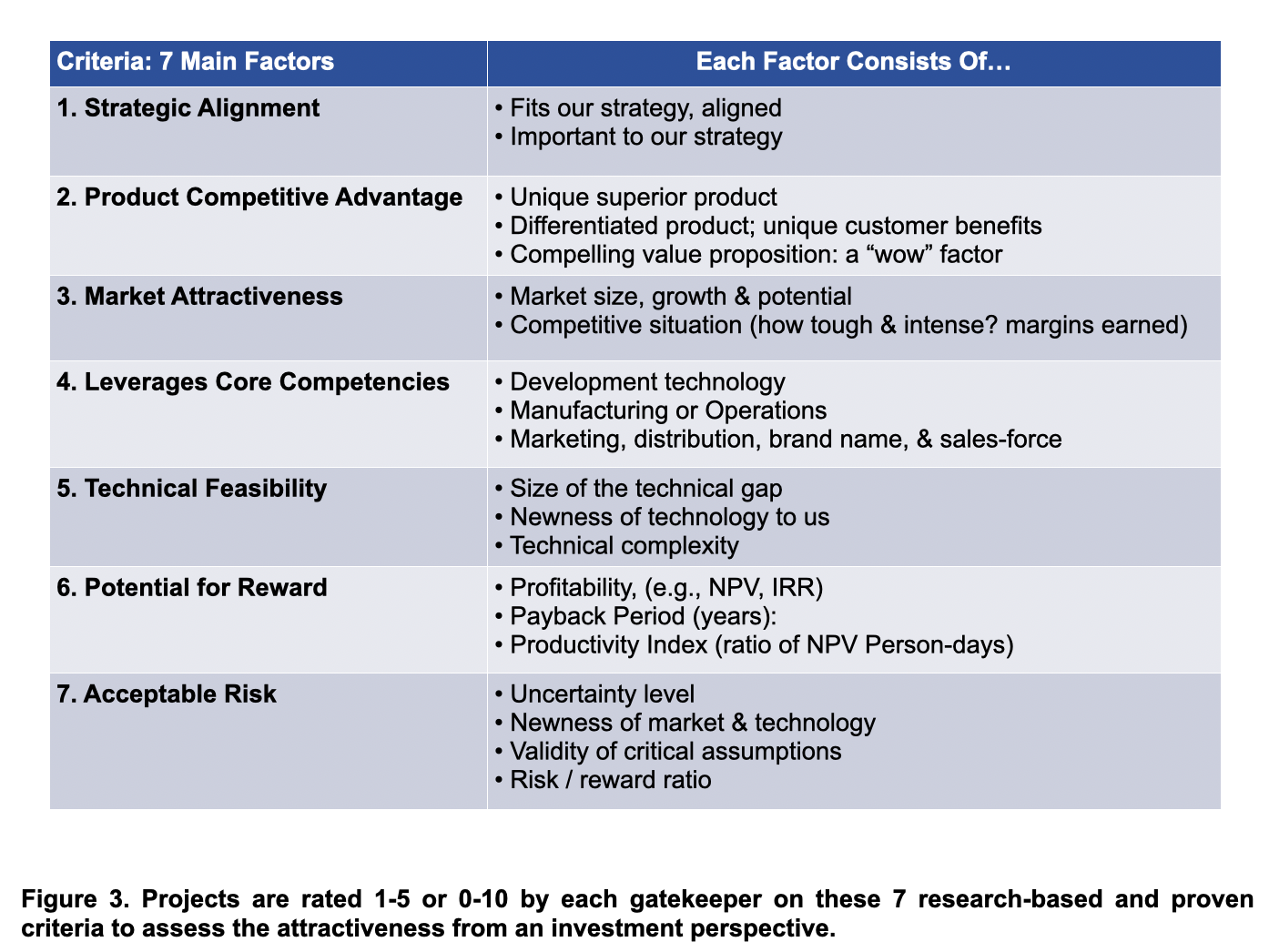
Qualitative Scoring Fashions: A scoring mannequin, comprised of a brief listing of qualitative screening standards, can be utilized along side monetary standards to enhance the standard of the gate resolution. Quite a few elements have been proven to correlate strongly with new product success and profitability, and ought to be used as standards.18,19 Because of this, research-based scoring fashions have been developed that predict new-product outcomes fairly effectively, as excessive as 83 % precisely, pre-Improvement.20 Most of the fashions had been initially developed privately inside companies, however lately, extra are discovered within the public area.21 Seven confirmed standards for such a scoring mannequin are in Determine 3.
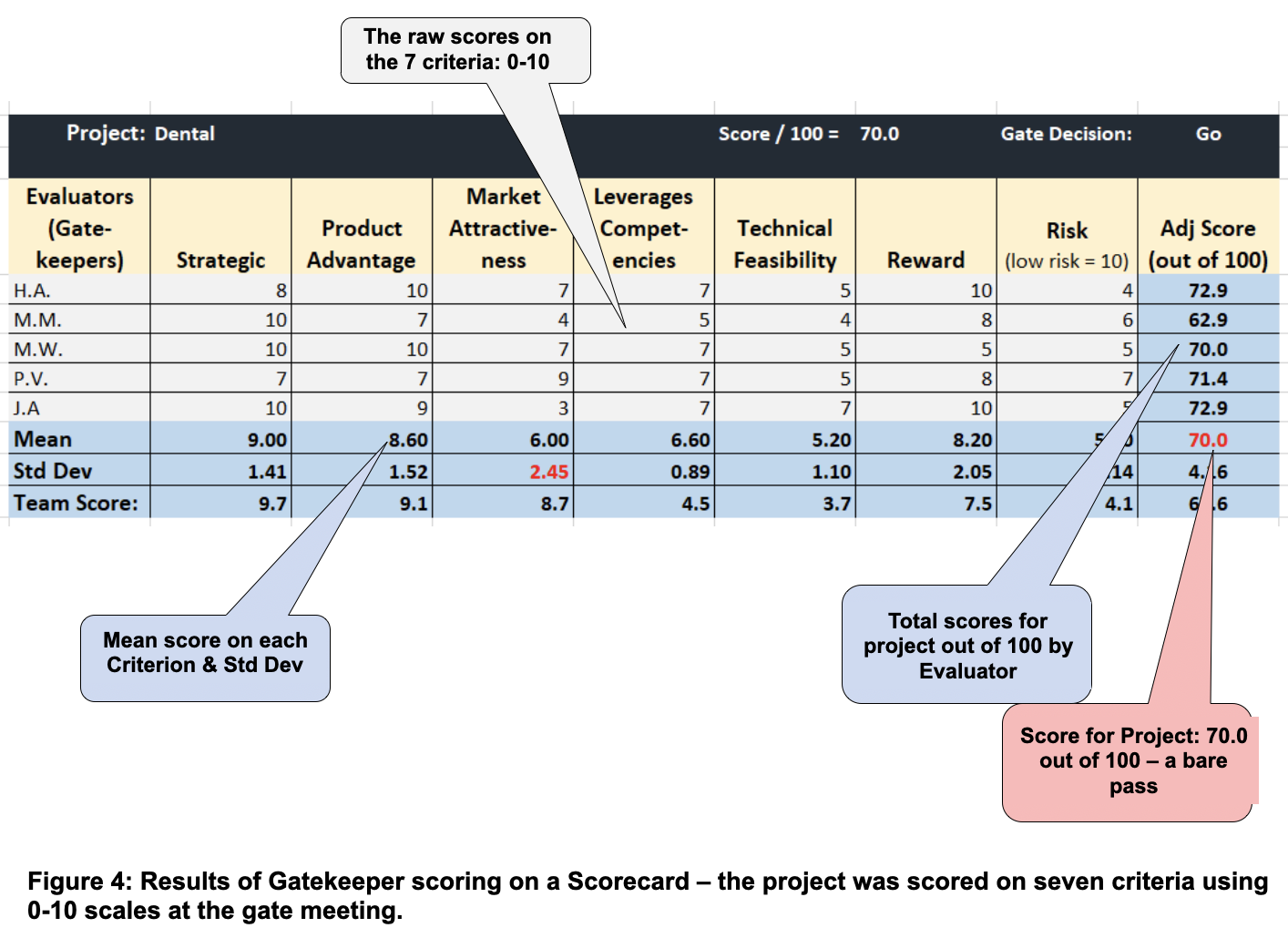
In apply at gate conferences, following an replace presentation of the undertaking by the undertaking workforce, every gatekeeper scores the undertaking on these standards utilizing a scorecard (normally on 0-10 or 1-5 scales). These gatekeeper scores are collected and displayed on the assembly room display screen (Determine 4); variations between gatekeepers are normally evident, and promote a strong dialogue and debate. Then the Go or Kill resolution is made, and if Go, the assets are dedicated (Within the instance in Determine 4, a rating of 65/100 is a “go”). This strategy is loosely based mostly on the Delphi technique, which has confirmed helpful when proof is missing or restricted (Delphi depends on “collective intelligence” of group members to collectively produce higher outcomes than anybody within the group might produce on their very own, leading to a greater resolution). This clear resolution course of yields a fruitful dialogue, and normally leads to extra considerate and higher Go/Kill selections.
Portfolio Critiques to Rank and Prioritize the Tasks
Portfolio critiques aren’t simply an opportunity for administration to get a fast replace on current initiatives, however a gathering of senior folks to handle three very important questions:
- Do we’ve got the correct prioritization of initiatives: Are one of the best initiatives actually on the high of the listing and getting the assets they advantage?
- Do we’ve got enough assets: Have we utilized sufficient assets to adequately useful resource all of the lively initiatives in our portfolio and get them achieved on time?
- Do we’ve got the correct steadiness and mixture of initiatives: Or do we’ve got too many “tweaks and modifications” that devour far too many assets, and starve the extra helpful initiatives?
The Productiveness Index to Rank Tasks
Rating initiatives by their NPVs or some related revenue metric is not the way in which to prioritize growth initiatives. The result’s a sub-optimal listing of initiatives. As an alternative, the Productiveness Index, launched above, is an efficient method to prioritize initiatives when there are constrained assets, which is normally the case.22 Recall from above: The Productiveness Index is just the worth of the undertaking divided by the constraining useful resource, normally person-days or {dollars}.
In apply at a portfolio evaluation, initiatives are power ranked 1 to N down the listing. Sources per undertaking are added up, and when the useful resource restrict is reached, a line is drawn: These initiatives beneath the road are killed or put on-hold, and their assets are re-allocated to the higher initiatives above the road. Rating initiatives by this Productiveness Index is one method to cull out the decrease “bang for buck” initiatives—they fall to the underside of the rating listing. Executed appropriately, this technique maximizes the worth of the event portfolio for a given useful resource spend.
Instance: Acme Firm has too many lively initiatives of their portfolio, and so initiatives are taking too lengthy.23 The portfolio supervisor produced a listing of the 16 lively main initiatives—Determine 5—which confirmed the precise assets going to initiatives (FTEs) and likewise what the undertaking chief had fairly requested. As shortly seen from Determine 5, the “useful resource demand” enormously exceeds the “useful resource provide:” 60.7 FTEs versus 26 FTEs. The full useful resource necessities for all 16 initiatives is 2.3 occasions the 26 FTEs obtainable! Little marvel that initiatives are working delayed. Additional, nearly all initiatives are under-resourced (precise versus wanted assets), with some initiatives having lower than one-half of an FTE assigned; and two exec-sponsored initiatives (Dental A and Pump, each circled) are consuming 66% of the assets.
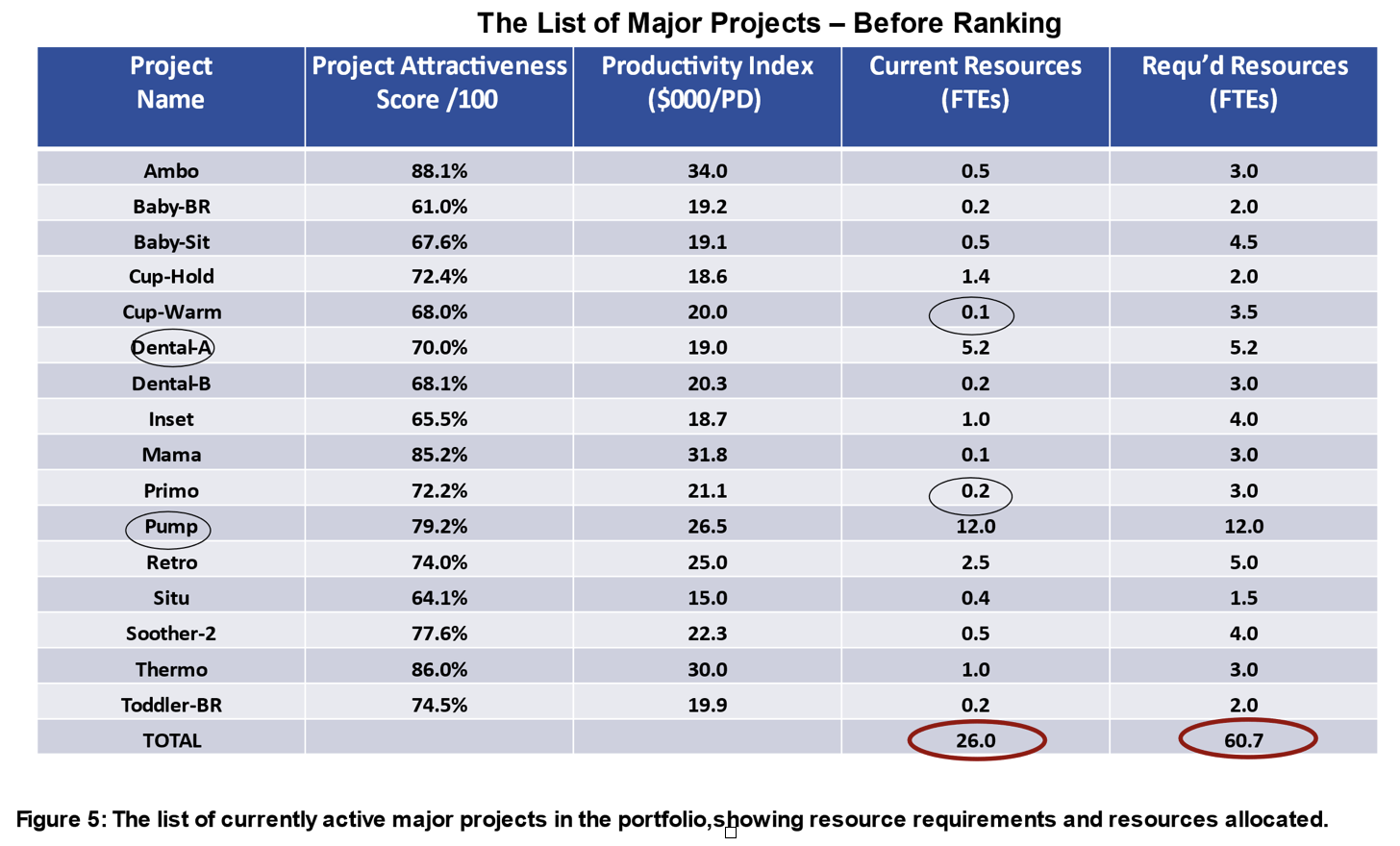
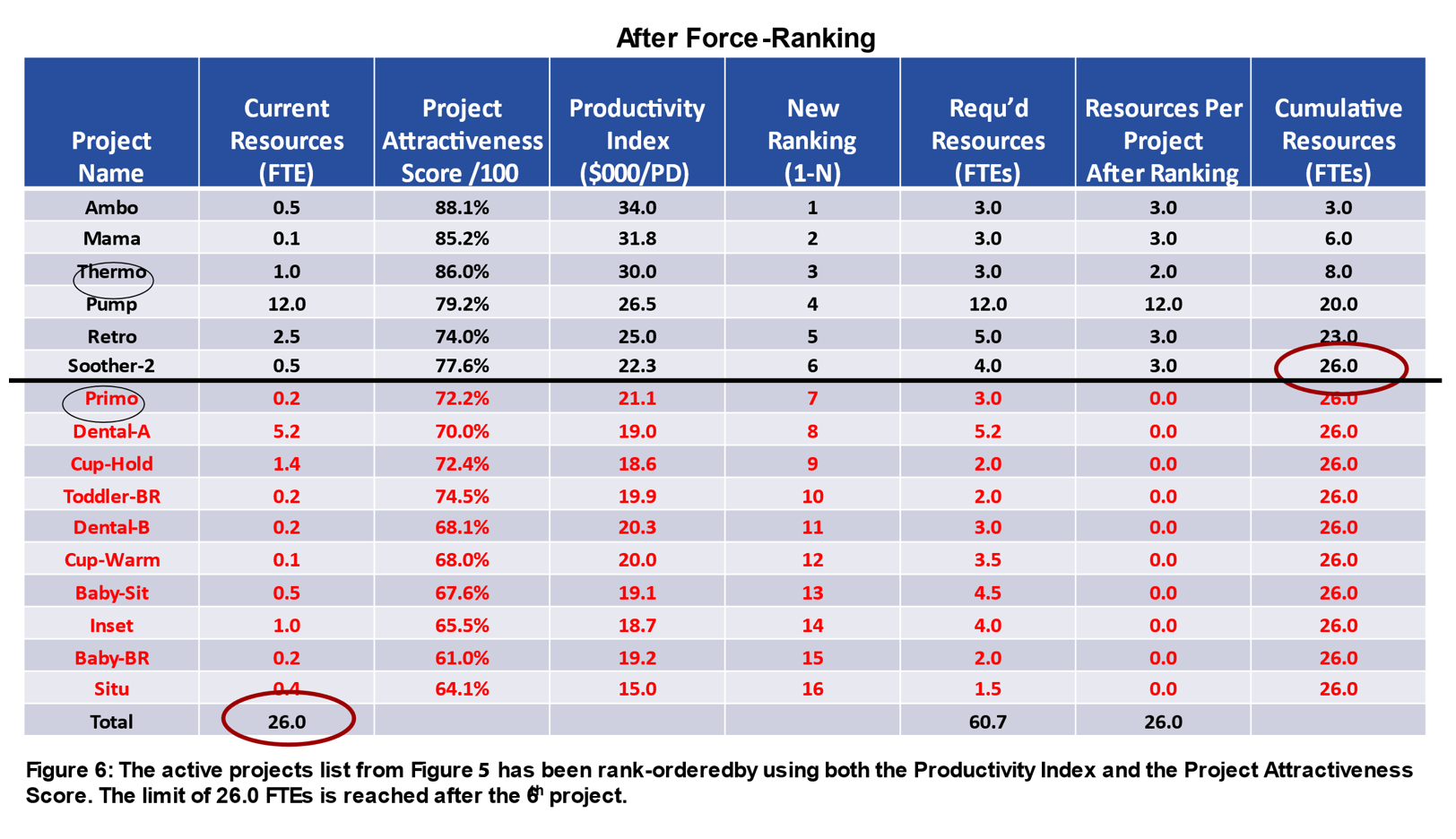
We then force-ranked the initiatives from finest to worst utilizing each the Productiveness Index and the Mission Attractiveness Rating (based mostly on a scorecard technique), each proven in Determine 5. The re-ranked result’s in Determine 6. After rating the initiatives and including up assets per undertaking (last column), the useful resource restrict is reached after the sixth undertaking. Thus, 10 of the 16 initiatives had been placed on maintain (proven in pink), and their assets re-allocated to the highest six initiatives. Because of this, excluding one exec-sponsored undertaking, the opposite 5 high precedence initiatives noticed their assets elevated by an element of three.0, and will now be accelerated. A easy process, however very efficient.
Strategic Buckets to Obtain the Proper Combine and Stability of Tasks
Strategic Buckets is a finest apply designed to maneuver the agency in direction of the right combination and steadiness of initiatives.24 Too typically, so many instant and small initiatives—fixes, modifications and tweaks—are underway that there are few assets left for the most important initiatives.
In utilizing Strategic Buckets, administration makes an annual strategic resolution to ascertain buckets of assets for several types of initiatives. This strategic strategy relies on the easy premise that “technique turns into actual once you begin spending cash”… so, make the spending (allocation) selections!
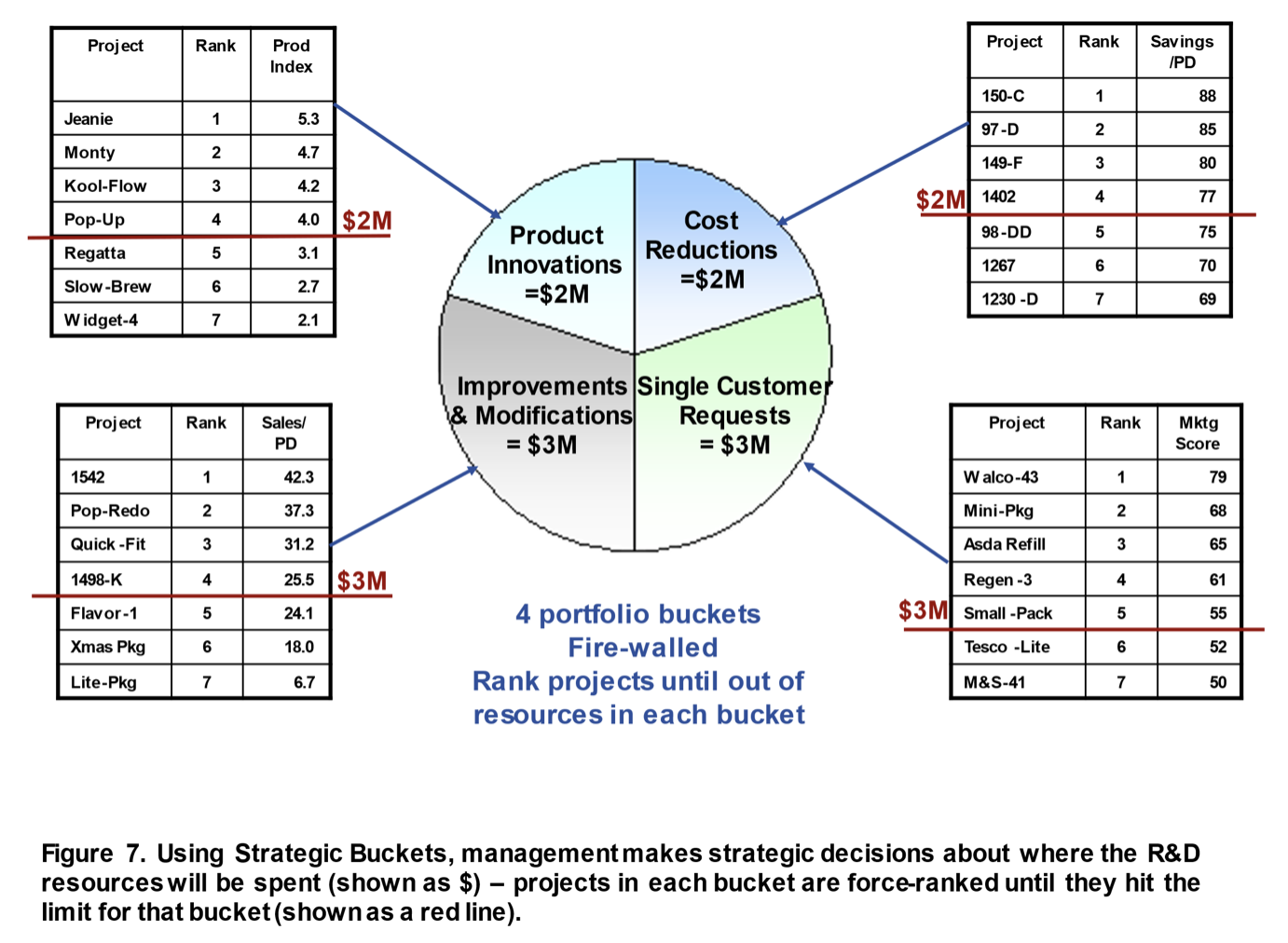
Right here’s the way it works:25 Varied classes or “buckets” of initiatives are outlined, from smaller enchancment and modification initiatives via to product improvements (Determine 7 ). Subsequent, the enterprise’s management workforce makes a strategic resolution about what quantity of R&D assets goes to every bucket, setting apart useful resource buckets for improvements versus enhancements versus single buyer requests, and so forth. The distribution of assets is dictated by the enterprise’s technique.
Lively and proposed growth initiatives are subsequent categorized by bucket and rank-ordered inside every bucket till there are not any extra assets in that bucket. Every bucket has its personal rating criterion. And dimensions apart from undertaking varieties can be used right here, though undertaking varieties is a well-liked dimension. For instance, useful resource splits will be by market sector, geography, expertise varieties, and product traces.
How does one decide the suitable break up of assets throughout undertaking varieties? No magic reply exists right here, any greater than there’s a single optimum break up amongst shares, bonds, and financial institution deposits in a person’s private funding portfolio. However the resolution have to be made. Failure to make a strategic resolution right here will lead to a break up based mostly on a sequence of advert hoc tactical selections made as the necessity arises. And this default possibility is normally unsuitable!
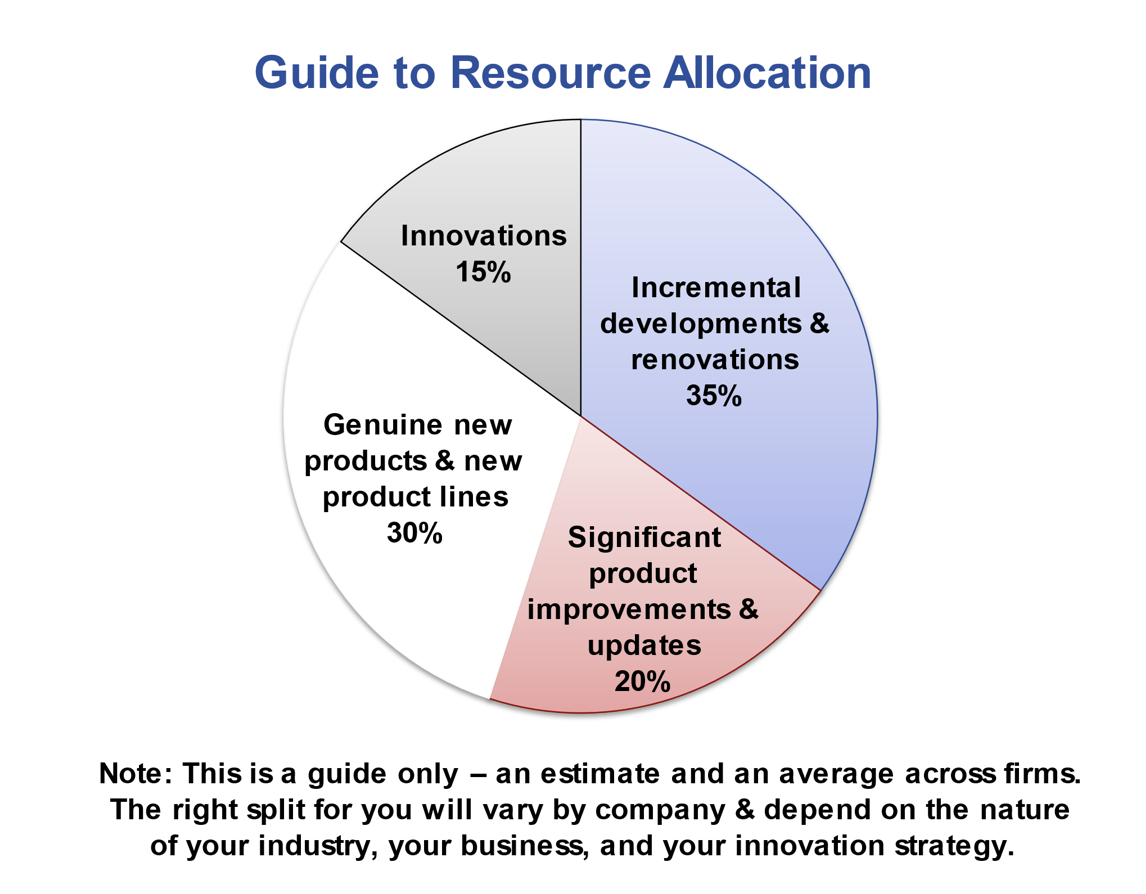
In deciding the optimum break up in your firm, begin with the present breakdown of assets, as decided by your current-state evaluation. Merely realizing the present useful resource break up—one thing that isn’t at all times seen in lots of companies—will recommend what the break up ought to be, for instance, that sure buckets ought to clearly have elevated assets and others ought to be decreased. Then take a look at your innovation technique and its objectives and goals. Contemplate too your historic track-record with totally different undertaking varieties. One other resolution enter is the place best-in-class companies spend their cash (a information, based mostly on increased performing companies, is proven in Determine 8).26
Instance: Senior administration in Beta Firm meets and critiques their present spending splits by undertaking sort. Minor initiatives appear to be consuming greater than they need to. A strategic evaluation ensues, together with a take a look at the efficiency of previous initiatives and the alternatives in every bucket. Then administration “votes” and decides on the break up proven in Determine 7 above (R&D in {dollars} per yr in every bucket).
Subsequent, lively initiatives are categorized by bucket, after which rank-ordered from finest to worst in that bucket, as in Determine 7, very similar to within the rating instance above. When the useful resource restrict is reached, a line is drawn: these initiatives beneath the road are both killed or put “on maintain.”
Notice that totally different standards are used for the rating in every bucket. In Determine 7, the Productiveness Index is used to rank the innovation initiatives, whereas value discount initiatives use an easier ratio (the cost-savings per person-days of labor).
When used over time, the strategy ensures that the initiatives “in” the portfolio and the spending breakdowns throughout buckets really mirror the strategic priorities of the enterprise. And assets are reserved for bolder initiatives: The strategy protects increased danger, innovation initiatives, as a result of they aren’t in comparison with predicable, smaller ones; initiatives are solely ranked in opposition to related initiatives inside their very own bucket, not throughout buckets. Moreover, the strategy limits the variety of initiatives inside every bucket: As soon as the useful resource restrict is hit, initiatives have to be placed on maintain or killed.
Making It Work
“Too many initiatives in our growth pipeline” is a standard drawback in business, and likewise is the basis reason for a lot of what ails new-product growth. When initiatives are under-resourced, essential duties are skipped, resembling doing the front-end homework, the voice-of buyer examine, or the additional technical work required to actually delight the client. And so the undertaking underperforms financially, or it misses its launch date.
Options do exist: The objective is to do fewer initiatives however higher initiatives, and useful resource them correctly. Approaches to attaining this are supplied: Some options give attention to particular person initiatives, resembling monitoring initiatives in actual time by monitoring the productiveness index; the pink flag system; monitoring assets going to every undertaking; and at last, more durable gates to kill weaker initiatives. Different options take a look at the whole portfolio of initiatives: These embrace the usage of Strategic Buckets to get the correct mix and numbers of initiatives, and portfolio critiques to force-rank initiatives, thereby eliminating decrease worth ones. Every of those options does take some effort, however then the price of persevering with with too many initiatives within the pipeline is large.
Concerning the Writer

Dr. Robert G. Cooper is ISBM Distinguished Analysis Fellow at Penn State College’s Smeal Faculty of Enterprise Administration, USA; and Professor Emeritus, DeGroote College of Enterprise, McMaster College, Canada. He pioneered the unique analysis that led to many groundbreaking discoveries, together with the Stage-Gate® Concept-to-Launch course of. He has spent greater than 30 years finding out the practices and pitfalls of three,000+ new product initiatives in hundreds of firms.
E-mail: robertcooper@cogeco.ca
Webpage: www.bobcooper.ca
References
- Cooper, R.G. & Sommer, A.F. “New-Product Portfolio Administration with Agile: Challenges and Options for Producers Utilizing Agile Improvement,” Analysis-Know-how Administration, 63:1, 2020, pp 29-36: http://www.bobcooper.ca
- Dalton. M. “Handle Pipeline Bandwidth to Keep away from Derailing New Merchandise,” Business Week, Aug 23, 2016: https://www.industryweek.com/process-improvement/manage-pipeline-bandwidth-avoid-derailing-new-products
- Thomke, S. & Reinertsen, D. “Six Myths of Product Improvement,” Harvard Enterprise Overview, 90:5,2012, pp 84-94.
- Edgett, S.J. “Portfolio Administration for Product Innovation,” PDMA Handbook of New Product Improvement, third version, ed. Ok. B. Kahn, Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2013, Ch 9, pp 154-166.
- Amaral, A. & Araújo, M. “Mission Portfolio Administration Phases: A Approach for Technique Alignment,” World Academy of Science, Engineering and Know-how Worldwide Journal of Economics and Administration Engineering, 3:10, 2009, pp 1919-1927.
- Elonen, S. & Artto, Ok.A. “Issues in Managing Inside Improvement Tasks in Multi-Mission Environments,” Worldwide Journal of Mission Administration, 21:6, 2003, pp 395-402.
- Cooper, R.G., Edgett, S.J. & Kleinschmidt E.J. “Benchmarking Finest NPD Practices-2: Technique, Sources and Portfolio Administration Practices,” Analysis-Know-how Administration, 47:3, Could-June 2004, pp 50-60.
- Meifort, A. “Innovation Portfolio Administration: A Synthesis and Analysis Agenda,” Creativity and Innovation Administration, 25:2, 2016, pp 251-269.
- Cooper, R.G., Edgett, S.J. & Kleinschmidt, E.J. “New Product Portfolio Administration: Practices and Efficiency,” Journal of Product Innovation Administration, 16, 1999, pp 333–350.
- PDMA Handbook of New Product Improvement, third version, ed. Ok. B. Kahn, Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2013, Glossary, p 461.
- Cooper & Sommer, endnote 1.
- Aberdeen Group. The Product Portfolio Administration Benchmark Report, 2006: https://www.plm.automation.siemens.com/zh_cn/Pictures/aberdeen_portfolio_mgmt_tcm78-5843.pdf
- From Cooper & Sommer, endnote 1.
- Cooper, R.G. Profitable at New Merchandise: Creating Worth Via Innovation, fifth version, New York, NY: Primary Books, Perseus Books Group, 2017, p 349.
- The time period “gates with tooth” comes from: Jenner, S. “‘Gates with Tooth’: Implementing a Centre of Excellence for Funding Choices,” Proceedings, First Worldwide Stage-Gate Convention, St. Petersburg Seaside, FL, 2007.
- PDMA attrition curve: Product Improvement & Administration Affiliation, Chicago IL.
- Based mostly on analyses of precise versus forecasted gross sales or earnings of NPD initiatives. One examine within the public area is from Procter & Gamble; the “50% success fee” is outlined as “Precise NPV/Forecasted NPV”: Mills, M. Implementing a Stage-Gate Course of at Procter & Gamble. Stage-Gate Management Summit, Convention, St. Petersburg Seaside, FL, 2007.
- Cooper, R. G. “New Merchandise—What Separates the Winners From the Losers and What Drives Success,” PDMA Handbook of New Product Improvement, third version, ed. Ok. B. Kahn, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. 2013, Ch 1, pp 25-33.
- Cooper, R. G. “The Drivers of Success in New-Product Improvement,” Industrial Advertising Administration, 76, Jan 2019, pp 36-47: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.07.005
- Bronnenberg, J.J.A.M. & van Engelen, M.L. “A Dutch Check With the NewProd Mannequin,” R&D Administration, 18:4: 1988, pp 321-332.
- Cooper, R.G. “Choosing Profitable New Merchandise: Utilizing the NewProd System,” Journal of Product Innovation Administration, 2:1, 1985, pp 34-44.
- Matheson, D., Matheson, J.E. & Menke, M.M. “Making Glorious R&D Choices,” Analysis Know-how Administration, 37:6, Nov-Dec 1994, pp 21-24.
- Cooper, R.G. “Accelerating Innovation: Classes from the Pandemic,” Journal of Product Innovation Administration, 38:2, March , 2021, pp 1-11: http://www.bobcooper.ca
- Cooper & Sommer, endnote 1.
- Cooper, R.G., “The place Are All of the Breakthrough New Merchandise? Utilizing Portfolio Administration to Enhance Innovation,” Analysis-Know-how Administration, 156:5, Sept-Oct 2013, pp 25-32.
- This information for the break up in assets relies on various sources; see for instance: Cooper, R.G., Edgett, S.J. & Kleinschmidt E.J, “Benchmarking Finest NPD Practices-2: Technique, Sources and Portfolio Administration Practices,” Analysis-Know-how Administration, 47: 3, Could-June 2004, pp 50-60. And: Industrial Analysis Institute, An replace to the 2004 Benchmarking Finest NPD Practices: Washington, DC: 2021.
Featured picture by way of Pixabay.


